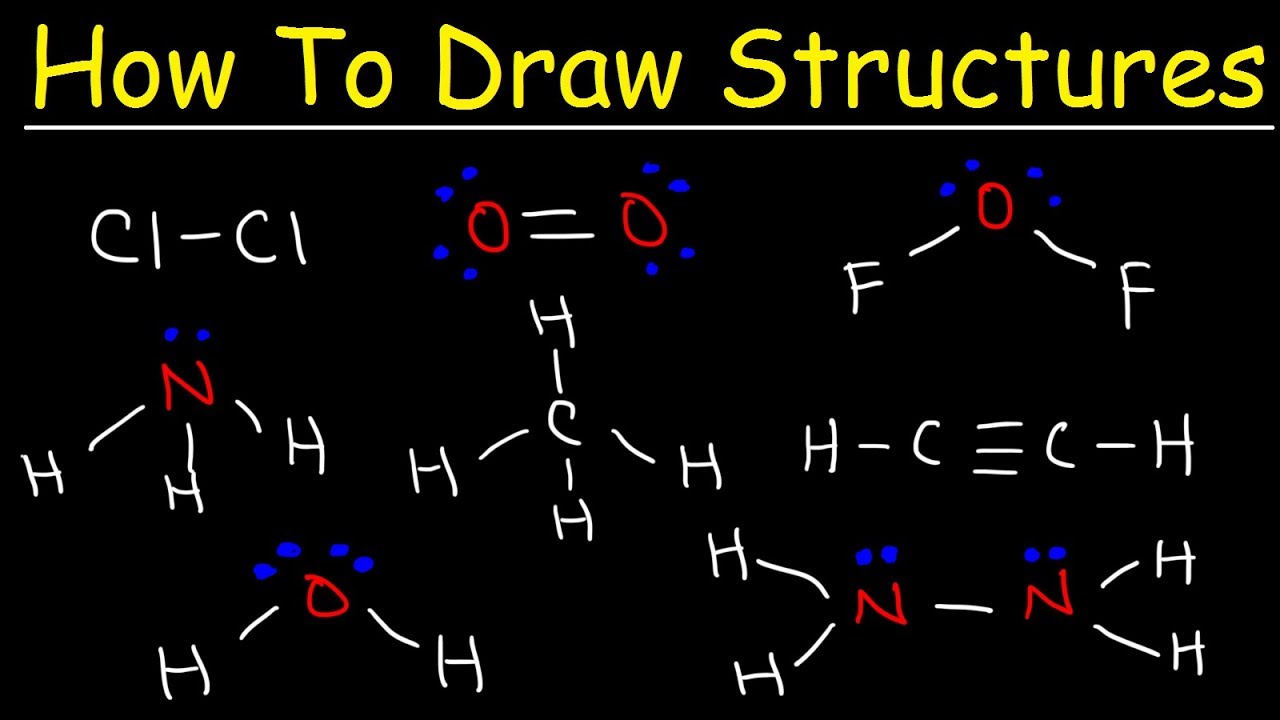

This chemistry video provides a basic introduction into how to draw lewis structures of common molecules such as Cl2, O2, OF2, CH4, NH3, H2O, C2H2, and N2H4. It contains a few examples and practice problems. Chemistry Basic Introduction and Final Exam Review: My Twitter Page: ...(read more)

LEARN MORE ABOUT: Treasury Inflation Protected Securities
REVEALED: Best Investment During Inflation
HOW TO INVEST IN GOLD: Gold IRA Investing
HOW TO INVEST IN SILVER: Silver IRA Investing
How To Draw Lewis Structures: A Step-by-Step Guide When studying chemistry, one of the fundamental skills you need to master is drawing Lewis structures. A Lewis structure is a representation of a molecule or an ion that shows the arrangement of atoms and electrons. By learning how to draw Lewis structures, you can better understand the bonding and structure of molecules. In this article, we will provide you with a step-by-step guide on how to draw Lewis structures. Step 1: Determine the Total Number of Valence Electrons Before you can start drawing the Lewis structure, you need to know the total number of valence electrons in the molecule or ion. The valence electrons are the electrons located in the outermost shell of an atom. To determine this number, you can refer to the periodic table. The columns (groups) in the periodic table generally indicate the number of valence electrons for each element. For example, elements in group 1 have one valence electron, while elements in group 2 have two valence electrons. Step 2: Identify the Central Atom The central atom is usually the least electronegative atom or the atom that forms the most bonds in the molecule. Hydrogen is typically never the central atom, and in most cases, carbon is the central atom for organic compounds. Step 3: Connect the Atoms with Single Bonds Next, connect the atoms with single bonds. Each bond consists of two electrons. Place the bonded atoms closer to each other, and the central atom should have a single bond with each surrounding atom. Step 4: Distribute the Remaining Electrons After connecting the atoms, distribute the remaining electrons around the atoms. Start by filling the octet (eight electrons) of each surrounding atom. Remember that hydrogen only needs two electrons to achieve a full outer shell. Fill the remaining electrons on the central atom. If there are still remaining electrons, distribute them by adding double or triple bonds, if necessary, to satisfy the octet rule. Step 5: Assess the Formal Charge Check the formal charge of each atom by subtracting the number of lone pair electrons and half the number of shared electrons from the number of valence electrons an atom normally has. The goal is to minimize the formal charges while maintaining a reasonable structure. Generally, a Lewis structure with small or no formal charges is more stable. Step 6: Check for Exceptions There are a few exceptions to the octet rule. Elements in the third period and beyond can expand their valence shells and accommodate more than eight electrons. This occurs when elements can use their empty d-orbitals to form additional bonds. Also, some compounds may have an odd number of valence electrons, which cannot be evenly distributed. Step 7: Refine the Lewis Structure After going through the above steps, refine the Lewis structure if necessary. Adjust the positions of atoms and electrons to minimize formal charges and maintain stability. Step 8: Evaluate the Resonance Structures In some cases, there may be multiple ways to draw the Lewis structure for a molecule or ion. These different structures are called resonance structures. Evaluate the resonance structures to see which one is more accurate or stable. By following these step-by-step instructions, you can effectively draw Lewis structures for various molecules and ions. Remember that practice makes perfect, so keep practicing and honing your skills until you become proficient in drawing Lewis structures. https://inflationprotection.org/a-step-by-step-guide-on-drawing-lewis-structures/?feed_id=114794&_unique_id=64a7290a464ba #Inflation #Retirement #GoldIRA #Wealth #Investing #basicintroduction #chemistry #examples #howtodrawlewisstructures #introduction #lewisstructures #molecules #practiceproblems #problems #TIPSBonds #basicintroduction #chemistry #examples #howtodrawlewisstructures #introduction #lewisstructures #molecules #practiceproblems #problems
Comments
Post a Comment